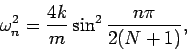Next: Exercise 5.7: propagation speed
Up: Coupled oscillators
Previous: Exercise 5.5: three coupled
- Choose
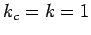 and
and 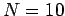 . Find the normal modes by applying an
external force to one of the particles and determine the resonant
frequencies. Drive the system for several periods of the external force and
compute the steady state amplitude of the displacement of each particle for
each value of
. Find the normal modes by applying an
external force to one of the particles and determine the resonant
frequencies. Drive the system for several periods of the external force and
compute the steady state amplitude of the displacement of each particle for
each value of 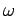 . Try values of
. Try values of 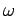 in the range
in the range
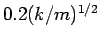 to
to 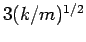 . If you think that you are close to a resonance, use
several other values of
. If you think that you are close to a resonance, use
several other values of 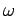 to obtain a better estimate. How many
normal modes are there?
to obtain a better estimate. How many
normal modes are there?
- Compare your results in part 1 with the analytic result
where 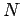 is the number of particles and the mode index is
is the number of particles and the mode index is 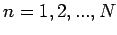 .
.
Adrian E. Feiguin
2004-06-01