Next: The Coulomb (Thomas-Fermi) functional
Up: Density Functional Theory
Previous: Some considerations about exchange
Functionals are mappings from function spaces to real or complex numbers. A general representation for a function 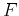 is
is
where the kernels 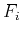 are general functions.
are general functions.
Now let
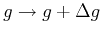 . To linear order in
. To linear order in 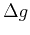 we obtain
we obtain
where we have assumed that the functions 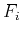 are symmetric functions of their arguments.
are symmetric functions of their arguments.
We can rewrite this equation as
![\begin{displaymath}
F[g+\Delta g] = f[g] + \int dx \frac {\delta F[g]}{\delta g(x)} \Delta g(x)
\end{displaymath}](img340.png) |
(137) |
where
In analogy, we find



Next: The Coulomb (Thomas-Fermi) functional
Up: Density Functional Theory
Previous: Some considerations about exchange
Adrian E. Feiguin
2009-11-04
![]() is
is
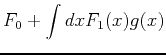
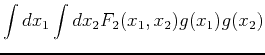
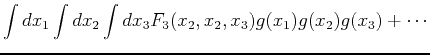
![]() . To linear order in
. To linear order in ![]() we obtain
we obtain
![$\displaystyle F[g] + \int dx F_1(x) \Delta g(x)$](img337.png)
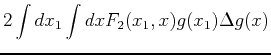
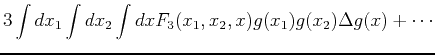
![\begin{displaymath}
F[g+\Delta g] = f[g] + \int dx \frac {\delta F[g]}{\delta g(x)} \Delta g(x)
\end{displaymath}](img340.png)
![$\displaystyle \frac {\delta F[g]}{\delta g(x)}$](img341.png)
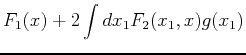
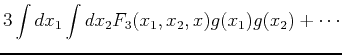
![$\displaystyle \frac {\delta^2 F[g]}{\delta g(x)\delta g(x')}$](img344.png)